Bisocor 5 | Tablet | 10 pcs
৳ 100.70
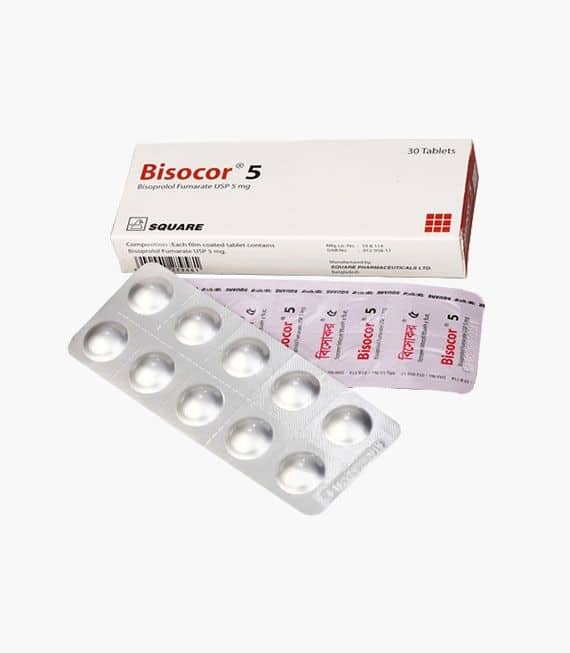
Brand Name: Bisocor Tablet
Generic: Bisoprolol Fumarate
5 mg
Manufacturer: Square Pharmaceuticals Ltd.
Unit Price: ৳ 10.07 (30’s pack: ৳ 302.10)
Indications
Therapeutic Class
Pharmacology
Dosage & Administration
Interaction
Contraindications
Side Effects
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy: Bisoprolol should not be used during pregnancy unless clearly necessary. If treatment with Bisoprolol is considered necessary, the uteroplacental blood flow and the foetal growth should be monitored. In case of harmful effects on pregnancy or the foetus, alternative treatment should be considered. The newborn infant must be closely monitored. Symptoms of hypoglycaemia and bradycardia are generally to be expected within the first 3 days.
Lactation: It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Therefore, breast-feeding is not recommended during administration of Bisoprolol.
Precautions & Warnings
Bisoprolol Fumarate must be used with caution in:
- Bronchospasm (bronchial asthma, obstructive airways diseases)
- Diabetes Mellitus with large fluctuations in blood glucose values; symptoms of hypoglycemia can be masked
- Strict fasting
- Ongoing desensitization therapy
- First degree AV block
- Prinzmetal’s angina
- Peripheral arterial occlusive disease (intensification of complaints might happen especially during the start of therapy)
- General anesthesia
Use in Special Populations
Pediatric Patients: There is no pediatric experience with Bisoprolol.
Geriatric Patients: It is not necessary to adjust the dose in the elderly, unless there is also significant renal or hepatic dysfunction.
Renal impairment: Reduce dose if eGFR less than 20 ml/ minute/ 1.73 m2 (max. 10 mg daily).
Hepatic impairment: Maximum 10 mg daily in severe impairment (hepatitis or cirrhosis).
Overdose Effects
Storage Conditions
| Generic Name | Bisoprolol Fumarate |
|---|---|
| Size | 5 mg |
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.