Clotinex 60 SC | Injection | 1 pcs
৳ 576.73
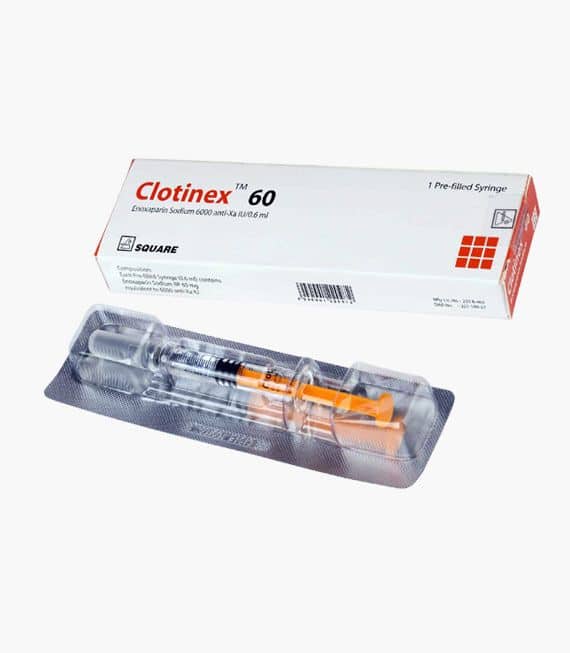
Brand Name: Clotinex SC Injection
Generic: Enoxaparin Sodium
6000 Anti-Xa IU/0.6 ml
Manufacturer: Square Pharmaceuticals Ltd.
0.6 ml pre-filled syringe: ৳ 576.73
Composition
Each 0.4 ml pre-filled syringe contains Enoxaparin Sodium 40 mg equivalent to 4000 anti-Xa III.
Each 0.6 ml pre-filled syringe contains Enoxaparin Sodium 60 mg equivalent to 6000 anti-Xa IU
Each 0.8 ml pre-filled syringe contains Enoxaparin Sodium 80 mg equivalent to 8000 anti-Xa IU
Indications
Enoxaparin is indicated in:
- Treatment of deep vein thrombosis, with or without pulmonary embolism.
- Treatment of unstable angina and non-Q-wave myocardial infarction, administered concurrently with aspirin.
- Prevention of thrombus formation in the extra-corporal circulation during haemodialysis.
- Prophylaxis of venous thromboembolic disease (prevention of blood clot formation in the veins), in particular those which may be associated with orthopedic or general surgery.
- Prophylaxis of venous thromboembolic disease in medical patients bedridden due to acute illness, including cardiac insufficiency, respiratory failure, severe infections, rheumatic diseases.
Therapeutic Class
Pharmacology
Dosage & Administration
Prophylaxis of venous thromboembolism: In patients with a low to moderate risk of venous thromboembolism the recommended dosage is 20 mg (2,000 IU) once daily by subcutaneous injection for 7 to 10 days, or until the risk of thromboembolism has diminished. In patients undergoing surgery, the initial dose should be given approximately 2 hours pre-operatively. In patients with a higher risk, such as in orthopaedic surgery, the dosage should be 40 mg (4,000 IU) daily by subcutaneous injection with the initial dose administered approximately 12 hours before surgery.
Prophylaxis of venous thromboembolism in medical patients: The recommended dose of enoxaparin sodium is 40 mg (4,000 IU) once daily by subcutaneous injection. Treatment with enoxaparin sodium is prescribed for a minimum of 6 days and continued until the return to full ambulation, for a maximum of 14 days.
Treatment of venous thromboembolism: Enoxaparin should be administered subcutaneously as a single daily injection of 1.5 mg/kg (150 IU/kg). Enoxaparin treatment is usually prescribed for at least 5 days and until adequate oral anticoagulation is established.
Treatment of unstable angina and non-Q-wave myocardial infarction: The recommended dose is 1 mg/kg Enoxaparin every 12 hours by subcutaneous injection, administered concurrently with oral aspirin (100 to 325 mg once daily). Treatment with Enoxaparin in these patients should be prescribed for a minimum of 2 days and continued until clinical stabilisation. The usual duration of treatment is 2 to 8 days.
Treatment of acute ST-segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction: The recommended dose of enoxaparin sodium is a single IV bolus of 30 mg plus a 1mg/kg SC dose followed by 1 mg/kg administered SC every 12 hours (max 100mg for the first two doses only, followed by 1 mg/kg dosing for the remaining doses).
Prevention of extracorporeal thrombus formation during haemodialysis: A dose equivalent to 1 mg/kg (100 IU/kg) introduced into the arterial line at the beginning of a dialysis session is usually sufficient for a 4 hour session. If fibrin rings are found, such as after a longer than normal session, a further dose of 0.5 to 1 mg/kg (50 to 100 IU/kg) may be given. For patients at a high risk of haemorrhage the dose should be reduced to 0.5 mg/kg (50 IU/kg) for double vascular access or 0.75 mg/kg (75 IU/kg) for single vascular access.
Interaction
Contraindications
Side Effects
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy: Pregnancy category B. In humans, there is no evidence that Enoxaparin Sodium crosses the placental barrier. As there are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women, Enoxaparin Sodium should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed. Pregnant women with mechanical prosthetic heart valves may be at a higher risk for thromboembolism.
Nursing mothers: It is not known whether Enoxaparin is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue Enoxaparin, taking into account the importance of Enoxaparin to the mother and the known benefits of nursing
Precautions & Warnings
Use in Special Populations
Dose in Renal Impairment: Although no dosage adjustment is recommended in patients with moderate (creatinine clearance: 30-50 ml/min) and mild (creatinine clearance: 50-80 ml/min) renal impairment, all such patients should be observed carefully for signs and symptoms of bleeding. For patients with severe (creatinine clearance <30 ml/min) renal impairment, following dosage adjustments are recommended: Prophylactic dose ranges: 2000 anti Xa IU once daily; Therapeutic dose ranges: 100 anti-Xa lU/kg once daily.
Dose in Hepatic Impairment: Caution should be used in hepatically impaired patients.
Elderly: For treatment of acute ST-segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction in elderly patients 75 years of age, do not use an initial IV bolus. Initiate dosing with 0.75 mg/kg SC every 12 hours (maximum 75 mg for the first two doses only, followed by 0.75 mg/kg dosing for the remaining doses). For other indications, no dosage adjustments are necessary in the elderly, unless kidney function is impaired.
Children: Not recommended, as dosage not established.
Overdose Effects
Storage Conditions
| Generic Name | Enoxaparin Sodium |
|---|---|
| Size | 0.6 ml |
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.